Implementing Advanced EIGRP
3 Advanced Basic Configuration
- 3.1 EIGRP over NBMA Networks
- 3.2 Enabling EIGRP Authentication
- 3.3 Best Practices
3.1 EIGRP over NBMA Networks
- Each Router is connected to a shared bandwidth
- This is called a PVC (permanent virtual connection)
- The connected participants uses numbers(DLCI) to communicate
- DLCI = data link connection identifier
- Communication over the cloud uses numbers instead of MAC addresses
- Each PVC has its own bandwidth limitation – called CIR(committed information rate)
- Different PVC’s can come in on a single physical interface
- the DLCIs numbers must be different in one Frame Relay cloud
- EIGRP can use “Pseudo-Broadcasts” or manual neighbors
- Broadcasts were denied
- Multicast messages were denied
- Multicast address were 224.0.0.10 to form neighbor relationship
- Pseudo Broadcast, because the broadcast were limited of the use of DLCIs. So it is called a Pseudo-Broadcast.
Later, there will be explained in the LAB. - With multipoint you save subnets. With point-to-point not
- Using the neighbor command in the routing process, you change a multicast address into a unicast address.
- One manual neighbor statement disables multicast.
- Split Horizon can be an issue
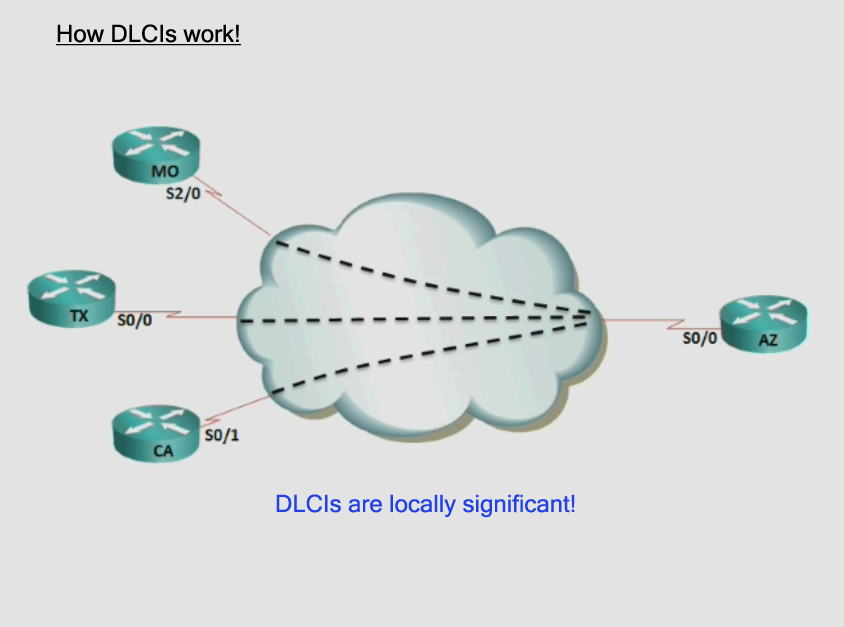
- figure 2 – Hub and Spoke. If a Router MD# sends a routing advertisement, the router AZ# who recieved this packet,
send the advertisement not back on the same interface, where he gets the advertisement. So – CA#
do not know everything about the networks from MD#. - Split Horizon – Disabled on physical interfaces
- Split Horizon – Enabled on Sub-interfaces
How DLCIs work
• X.25 (this was the first protocol of frame relay – followed by)
• ATM
• MPLS
Frame Relay PVC Design
How EIGRP handles NBMA
EIGRP Frame Relay Configuration
LAB Configuration
Objectives
• Configure EIGRP using AS 25 for the shown network. All networks should be announced via EIGRP
• Each office should generate an efficient EIGRP summary route to minimize routing table entries.
• Configure the HQ router to utilize up to 30% more of the allocated serial interface bandwidth then
3.2 Enabling EIGRP Authentication
-
• Enable authentication between all EIGRP routers. You should use two authentication keys:
3.3 Best Practices
- 3.3.1 Eavesdropping on EIGRP neighbors
- 3.3.2 Understanding the Query Process
- 1. Summary Routes
- .2 stub configuration
3.3.1 Eavesdropping on EIGRP neighbors
3.3.2 Understanding the Query Process
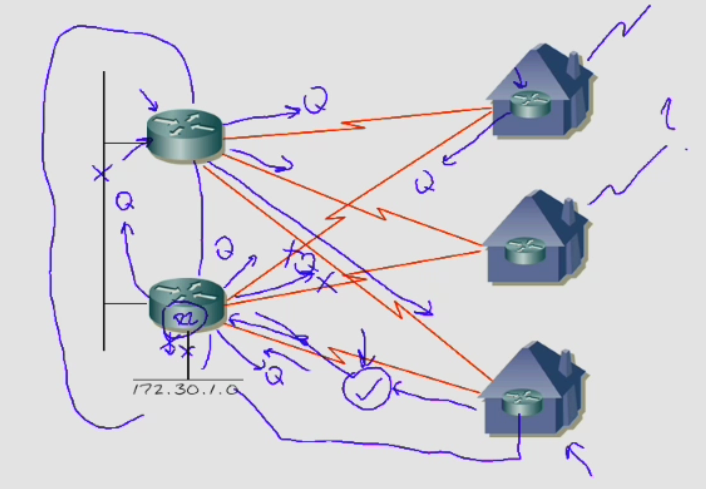
Look at figure 3.
When network 172.30.1.0 goes down, R2# send a query messages to all Routers and so on.
This causes an enormous control traffic of eigrp. R2 keep in for minimum 3 minutes in stuck in active mode. All other Routers reply with a Query Reply.
There are two methods to correct this problem.
1. The summary route will be send with a query to a neighbors router. But they don’t reply with a query,
2. Go into the router process for eigrp 25 and configure a stub.
-
R2(config-router)#eigrp stub ?
connected Do advertise connected routes
leak-map Allow dynamic prefixes based on the leak-map
receive-only Set IP-EIGRP as receive only neighbor
redistributed Do advertise redistributed routes
static Do advertise static routes
summary Do advertise summary routes
R2(config-router)#eigrp stub
If you hit enter, the default value is ‘connected’ and ‘summary’